The True Origins of Human Beings - Can You Handle It?
Starting with the Sumerians, the first great culture 6,000 years ago that spawned the Bablylonians, Persians, and Assyrians, through ALL subsequent "Intelligent advanced civilizations" and "non-advanced" indigenous cultures including the American Indians of North America, Mayan and Inca empires of South America, Aborigines of Australia, ancient Chinese and Hindu text scriptures from the Far East, Egyptians, of the Middle East, Dogons of Africa, and the Greek and Roman Gods of "mythology", every culture accepted for a fact that heavenly beings (Or Gods) had created Man kind - homosapiens- (In their own likeness, no less). Some coincidence to be a "myth", huh? To read more about the above mentioned myths, and view petrographs/petroglyphs from around the globe,
 Native American folklore, where legends of "Star Beings" can be harvested from the American Southwest to Tierra Del Fuego. In story-telling traditions dating back to antiquity, the gods once descended from heaven to impregnate barren females in remote villages. Mothers bearing these strange seeds would then nurture and raise the "Star Children" until the age of six or thereabouts, when the gods would return to reclaim their progeny, leaving villagers staring up into the infinite night. Every pre-christian culture has a similar tale.
Native American folklore, where legends of "Star Beings" can be harvested from the American Southwest to Tierra Del Fuego. In story-telling traditions dating back to antiquity, the gods once descended from heaven to impregnate barren females in remote villages. Mothers bearing these strange seeds would then nurture and raise the "Star Children" until the age of six or thereabouts, when the gods would return to reclaim their progeny, leaving villagers staring up into the infinite night. Every pre-christian culture has a similar tale.
The "Missing Link" has evaded science to date. The ultimate enigma in seeking the answer to mankind's most puzzling question: Who are we, and where did we come from? The orthodox explanation, largely derived from Charles Darwin is that humans evolved from apes by way of some intermediate species.
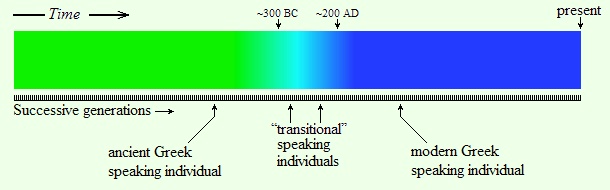
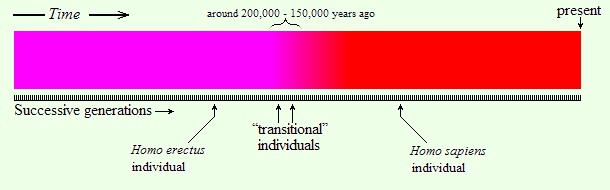
But evolution cannot account for the appearance of *Homo sapiens*, which happened virtually overnight instead of the millions of years evolution requires and with no evidence of earlier stages that would indicate a gradual change from *Homo erectus*. The hominid of the genus *Homo* is a product of evolution. But *Homo sapiens* is the product of some sudden evolutionary event. He appeared inexplicably some 300,000 years ago, millions of years too soon. The scholars have no explanation. But I do. The Sumerians and Babylonian texts do, the Old Testament does. *Homo sapiens*-- modern man-- was brought about by the ancient gods.
 Native American folklore, where legends of "Star Beings" can be harvested from the American Southwest to Tierra Del Fuego. In story-telling traditions dating back to antiquity, the gods once descended from heaven to impregnate barren females in remote villages. Mothers bearing these strange seeds would then nurture and raise the "Star Children" until the age of six or thereabouts, when the gods would return to reclaim their progeny, leaving villagers staring up into the infinite night. Every pre-christian culture has a similar tale.
Native American folklore, where legends of "Star Beings" can be harvested from the American Southwest to Tierra Del Fuego. In story-telling traditions dating back to antiquity, the gods once descended from heaven to impregnate barren females in remote villages. Mothers bearing these strange seeds would then nurture and raise the "Star Children" until the age of six or thereabouts, when the gods would return to reclaim their progeny, leaving villagers staring up into the infinite night. Every pre-christian culture has a similar tale.The "Missing Link" has evaded science to date. The ultimate enigma in seeking the answer to mankind's most puzzling question: Who are we, and where did we come from? The orthodox explanation, largely derived from Charles Darwin is that humans evolved from apes by way of some intermediate species.
But evolution cannot account for the appearance of *Homo sapiens*, which happened virtually overnight instead of the millions of years evolution requires and with no evidence of earlier stages that would indicate a gradual change from *Homo erectus*. The hominid of the genus *Homo* is a product of evolution. But *Homo sapiens* is the product of some sudden evolutionary event. He appeared inexplicably some 300,000 years ago, millions of years too soon. The scholars have no explanation. But I do. The Sumerians and Babylonian texts do, the Old Testament does. *Homo sapiens*-- modern man-- was brought about by the ancient gods.
So Why Not Reveal The Truth? Could You Hande It?
 A peek into the mind of government relating to the UFO/ET phenomenon and the processes at work on the community of nations is best described by Dr. Pierre Guerin an astronomer associated with the French GEPAN (Study Group Into Unidentified Atmospheric Phenomenon). Dr. Guerin feels there is an intelligence behind the UFO phenomenon and it is not human. Governments of earth understand that this intelligence coexists on the planet with humanity. There is a very high possibility that this intelligence is responsible for the creation of humanity. The impact of this truth on the world community if it became widely known would undermine the ability of the nations of Earth to maintain geopolitical order.[27] Dr. Pierre Guerin's reflections if true, compromise humanities evolutionary and historical self-perception and undermines all major human institutions worldwide. Dr. Guerin's views give us insight to the common denominator that allowed a worldwide cover-up of the UFO phenomenon's reality to evolve and the reasons for the continued maintenance of this policy.
A peek into the mind of government relating to the UFO/ET phenomenon and the processes at work on the community of nations is best described by Dr. Pierre Guerin an astronomer associated with the French GEPAN (Study Group Into Unidentified Atmospheric Phenomenon). Dr. Guerin feels there is an intelligence behind the UFO phenomenon and it is not human. Governments of earth understand that this intelligence coexists on the planet with humanity. There is a very high possibility that this intelligence is responsible for the creation of humanity. The impact of this truth on the world community if it became widely known would undermine the ability of the nations of Earth to maintain geopolitical order.[27] Dr. Pierre Guerin's reflections if true, compromise humanities evolutionary and historical self-perception and undermines all major human institutions worldwide. Dr. Guerin's views give us insight to the common denominator that allowed a worldwide cover-up of the UFO phenomenon's reality to evolve and the reasons for the continued maintenance of this policy.Former CIA official Victor Marchetti spelled out indirectly in 1979 everything the American people needed to know about the UFO phenomenon. His reflections are not far distanced from what Dr. Pierre Guerin described as the reason for the coverup. According to Marchetti, "We have, indeed, been contacted......and the U.S. government, in collusion with other national powers of the Earth, is determined to keep this information from the general public..."
"The purpose of the international conspiracy is to maintain a workable stability among the nations of the world and for them, in turn, to retain institutional control over their respective populations. Thus, for these governments to admit that there are beings from outerspace... with mentalities and technological capabilities obviously far superior to ours, could, once fully perceived by the average person, erode the foundations of the earth's traditional power structure. Political and legal systems, religions, economic and social institutions could all become meaningless in the mind of the public. The national oligarchical establishments, even civilization as we now know it, could collapse into anarchy... Such extreme conclusions are not necessarily valid, but they probably accurately reflect the fears of the 'ruling class' of the major nations, whose leaders (particularly those in the intelligence business) have always advocated excessive governmental secrecy as being necessary to preserve national security.
If beings from another world did visit our ancient ancestors, those offworld entities would have certainly been included in the legends of civilizations the world over and, sure enough, strange visitors are found in legends and religions from every corner of the earth be it Biblical angels or the warring sky people from ancient India. These "gods" had seemingly magical powers, unsurpassed wisdom and brought special gifts and experiences to those with which they came into contact.
 What actually transpired was that the original Mesopotamian writings were recorded as history. This history was later rewritten to form a base for foreign religious cults--first Judaism and then Christianity. The corrupted dogma of the religions then became established as 'history' and because the contrived dogma (the new approved history) was so different from the original writings, the early first-hand records were labeled 'mythology.'
What actually transpired was that the original Mesopotamian writings were recorded as history. This history was later rewritten to form a base for foreign religious cults--first Judaism and then Christianity. The corrupted dogma of the religions then became established as 'history' and because the contrived dogma (the new approved history) was so different from the original writings, the early first-hand records were labeled 'mythology.'But that would mean challenging the very traditional Judeo-Christian-Muslim concept of "God"!!! No easy task, given the power, properties, money and 'god-spell attitude' presently existing on Planet Earth. Maybe the Buddhists, Hindus, American Indians, Tibetans, Mayan, Inca, Aztec and other theories of creation could also be added. An Intercultural Institute of Evolutionary Creationism - IIEC! Yeah, that's it!
 All over the planet, you find the ancient legends and accounts of "gods" from another world who interbred with humanity to create a hybrid network of bloodlines. Many claim that they actually created humanity by splicing their genes with that of neanderthal to make you and I. Certainly would solve the "missing link" debate as the timeline is right on. The Old Testament, for example, talks about the "Sons of God" who interbred with the daughters of men to create the hybrid race, the Nefilim. Before it was translated into English, that passage read "the sons of the gods", plural. But the Bible accounts are only one of so many that describe the same theme.
All over the planet, you find the ancient legends and accounts of "gods" from another world who interbred with humanity to create a hybrid network of bloodlines. Many claim that they actually created humanity by splicing their genes with that of neanderthal to make you and I. Certainly would solve the "missing link" debate as the timeline is right on. The Old Testament, for example, talks about the "Sons of God" who interbred with the daughters of men to create the hybrid race, the Nefilim. Before it was translated into English, that passage read "the sons of the gods", plural. But the Bible accounts are only one of so many that describe the same theme.The Sumerian clay tablets, found in what we now call Iraq in the middle of the 19th century, tell a similar story. It is estimated they were buried around 2,000 BC, but the stories they tell go back long before that. The tablets talk of a race of "gods" from another world who brought advanced knowledge to the planet and interbred with humans to create hybrid bloodlines. These "gods" are called in the tablets, the "Anunnaki", which apparently translates as "those who from heaven to earth came."
The ancient accounts tell us that these hybrid bloodlines, the fusion of the genes of selected humans with those of the "gods", were put into the positions of ruling royal power, especially in the ancient Near and Middle East, in advanced cultures like Sumer, Babylon, and Egypt. Now, 20 years ago, had I discussed this, it would have been immediately perceived as nutty. But now that we've mapped the human gnome, we actually have the same technology that could perform the exact same scenario. We can now fuse genes and make countless new species, and make clones of anything with a DNA strand. Doesn't seem so far fetched anymore, would you not agree?TaDa! Missing link explained! And no donation required! :)
Could the Ancients Fly?



Throughout history there have been many common myths and legends of flying machines or devices, the familiar flying carpets of ancient Arabia; Bi-lical figures such as Ezekiel and Solomon flying from place to place and the magical chariots, or Vimanas, of ancient India and China.
There are many Chinese legends of flight, including a legendary flying chariot belonging to an ancient Chinese prince and the more recent Wan Hoo--of the 15th century A.D. or so. He allegedly built a sturdy wooden framework around a comfortable chair and attached 47 skyrockets to the back of the seat. Atop it he fastened two large kites. After strapping himself to the chair, he raised his hand and servants carrying blazing torches advanced toward the vehicle and ignited the skyrockets. A moment later there was a mighty blast, followed by an impressive cloud of black smoke. Wan Hoo vanished, leaving nothing behind but a legend.
Among the more famous ancient texts that mention aerial cars (Vimanas) are the Ramayana and Mahabharata. Other lesser known texts include the Samarangana Sutra-dhara, the Yuktikalpataru of Bhoja ( 12th century A.D.) the Mayamatam (attributed to the architect Maya celebrated in the Mahabharata), the Rig Veda, the Yajurveda and the Ataharvaveda.

According to the Indian historian Ramachandra Dikshitar who wrote the still classic text on ancient Indian warfare, other texts which mention aerial vehicles and travels are the Satapathya Brahmanas; the Rig Veda Samhita; the Harivamsa; the Makandeya Purana; the Visnu Purana; the Vikramaurvasiya; the Uttararamacarita; the Harsacarita; the Tamil text Jivakocintamani; and the Samaranganasutradhara. In the Manusa, the most elaborate details for building aerial machines are set down. The Samarangana Sutradhara says that they were made of light mterial, with a strong, well-shaped body. Iron, copper, mercury and lead were used in their construction. They could fly to great distances and were propelled through air by motors.
The Samarangana Sutradhara text devotes 230 stanzas to the building of these machines, and their uses in peace and war: Strong and durable must the body be made, like a great flying bird, of light material. Inside it one must place the Mercury-engine with its iron heating apparatus beneath. By means of the power latent in the mercury which sets the driving whirlwind in motion, a man sitting inside may travel a great distance in the sky in a most marvelous manner.
 Similarly by using the prescribed processes one can build a vimana as large as the temple of the G-d-in-motion. Four strong mercury containers must be built into the interior structure. When these have been heated by controlled fire from iron containers, the vimana develops thunder-power through the mercury. And at once it becomes a pearl in the sky.
Similarly by using the prescribed processes one can build a vimana as large as the temple of the G-d-in-motion. Four strong mercury containers must be built into the interior structure. When these have been heated by controlled fire from iron containers, the vimana develops thunder-power through the mercury. And at once it becomes a pearl in the sky.Moreover, if this iron engine with properly welded joints be filled with mercury, and the fire be conducted to the upper part it develops power with the roar of a lion. The Ramayana describes a vimana as a double-deck, circular (cylindrical) aircraft with portholes and a dome. It flew with the speed of the wind and gave forth a melodious sound (a humming noise?). Ancient Indian texts on Vimanas are so numerous it would take several books to relate what they have to say. The ancient Indians themselves wrote entire flight manuals on the control of various types of Vimanas, of which there were basically four: the Shakuna Vimana, the Sundara Vimana, the Rukma Vimana and the Tripura Vimana.
 The Vaimanika Sastra is perhaps the most important ancient text on Vimanas known to exist. It was first reported to have been found in 1918 in the Baroda Royal Sanskrit Library. Baroda is located north of Bombay and south of Ahmedabad in Gujerat. No earlier copies have been reported, however, Swami Dayananda Saraswati in his comprehensive treatise on the Rig Veda dated 1875 references the Vaimanaik Sastra in his commentary, as well as other manuscripts on Vimanas.
The Vaimanika Sastra is perhaps the most important ancient text on Vimanas known to exist. It was first reported to have been found in 1918 in the Baroda Royal Sanskrit Library. Baroda is located north of Bombay and south of Ahmedabad in Gujerat. No earlier copies have been reported, however, Swami Dayananda Saraswati in his comprehensive treatise on the Rig Veda dated 1875 references the Vaimanaik Sastra in his commentary, as well as other manuscripts on Vimanas.The Vaimanika Sastra refers to 97 past works and authorities, of which at least 20 works deal with the mechanism of aerial Flying Machines, but none of these works are now traceable. Says Sanskrit literature professor Dileep Kumar Kanjilal, Ph.D. of the West Bengal Senior Educational Service, Since the transcripts of the work date from early 20th century the authenticity of the Vail Sastra may be pertinently questioned. On careful analysis it has been found that the work retained some antique features pertaining to an old Sastra. Like the Sutras of Panini the rules have been laid down in an aphoristic style with the explanation couched in Vrittis and Karikas.
The Sutra style is to be found in the earliest works on grammar, Smrti and Philosophy, while the use of Karikas is as old as Batsyayana, Kautilya and others of the early Ch-istian era. Bharadwaja as the author of a Srauta Satra and Smrti work is well-known and a sage Bharadwaja as the seer of the 6th Mandala of the Rig Veda is also well-known. Panini also referred to him in VII. II.63. Kautilya had also shown that Bharadwaja was an ancient author on politics. The Mbh. (Mahabharata, Santiparva Ch. 58.3) refers to Bharadwaja as an author on politics. Authors on politics have very often been found to have written on the technical sciences also. The genuineness, therefore, of any treatise on technical sciences composed by Bharadwaja cannot be ignored.
Says the Vaimanika Sastra about itself: In this book are described in 8 pregnant and captivating chapters, the arts of manufacturing various types of Aeroplanes of smooth and comfortable travel in the sky, as a unifying force for the Universe, contributive to the well-being of mankind.
 That which can go by its own force, like a bird, on earth, or water, or air, is called Vimana.' That which can travel in the sky, from place to place, land to land, or globe to globe, is called Vimana by scientists in Aeronautics. The ancient manuscript claims to give:
That which can go by its own force, like a bird, on earth, or water, or air, is called Vimana.' That which can travel in the sky, from place to place, land to land, or globe to globe, is called Vimana by scientists in Aeronautics. The ancient manuscript claims to give:- The secret of constructing aeroplanes, which will not break, which cannot be cut, will not catch fire, and cannot be destroyed.
- The secret of making planes motionless.
- The secret of making planes invisible.
- The secret of hearing conversations and other sounds in enemy planes.
- The secret of receiving photographs of the interior of enemy planes.
- The secret of ascertaining the direction of enemy planes approach.
- The secret of making persons in enemy planes lose consciousness.
- The secret of destroying enemy planes.
The India of 15,000 years ago is sometimes known as the Rama Empire, a land that was contemporary with Atlantis. A huge wealth of texts still extant in India testify to the extremely advanced civilization that is said by these texts to go back over 26,000 years. Terrible w-rs and subsequent earth changes destroyed these civilizations, leaving only isolated pockets of civilization.
The devastating wa-s of the Ramayana and particularly of the Mahabharata are said to have been the culmination of the terrible -ars of the last Kali Yuga. The dating process is difficult, in that there is no exact way to date the yugas because there are cycles within cycles and yugas within yugas. A greater yuga cycle is said to last 6000 years while a smaller yuga cycle is only 360 years in the theory expounded by Dr. Kunwarlal Jain Vyas. His papers said that Rama belongs to the twenty-fourth small yuga cycle and that there is an interval of 71 cycles between Manu and Mahabharata period, which comes out to be 26,000 years.


The legacy of Atlantis, the ancient Rama Empire and Vimanas reaches us up to today. The mysterious airship wave of the 1890s may well have been a sighting of ancient craft, still in working order, meandering slowly over the pre-flight world of late 19th century America.
In the late years of the last century, a number of unusual airship sightings were made which may well have been of Vimana craft. In 1873 at Bonham, Texas, workers in a cotton field suddenly saw a shiny, silver object that came streaking down from the sky at them. Terrified, they ran away, while the great silvery serpent, as some people described it, swung around and dived at them again. A team of horses ran away, the driver was thrown beneath the wheels of the wagon and ki-led. A few hours later that same day in Fort Riley, Kansas, a similar airship swooped down out of the skies at a cavalry parade and terrorized the horses to such an extent that the cavalry drill ended in a tumult.
The great Airship Flap of 1897 actually started in November, 1896 in San Francisco, California when hundreds of residents saw a large, elongated, dark object that used brilliant searchlights and moved against the wind, traveling northwest across Oakland. A few hours later reports came from other northern California cities; Santa Rosa, Chico, Sacramento and Red Bluff, all describing what appears to be the same airship, a cigar-shaped craft. It is quite possible that this craft was heading for Mount Shasta in northern California.
The airship moved very slowly and majestically, flying low at times, and at night, shining its powerful searchlight on the ground. It is worth noting here, as Jacques Vallee did in his book Dimensions, that the airship could do exactly as it cared to, because unlike today, it ran no risk of being pursued. There were no jet squadrons to be scrambled after the aerial intruder, nor anti-aircraft guns or surface to air missiles to shoot down this trespassing craft in the sky.
A question sometimes asked by Vimanas researchers is whether the ancient Indians and Atlanteans ever went to our moon or to Mars? If mankind had such craft in ancient times, would they have created bases on the moon and Mars just as we are planning to do today? If they had set up permanent bases, would they still be occupying them today?
Check back soon! We'll be adding data from many of our sites including amazing photo's of petroglyphs and petrographs from all over the planet that will certainly blow your mind.
REFER: Source